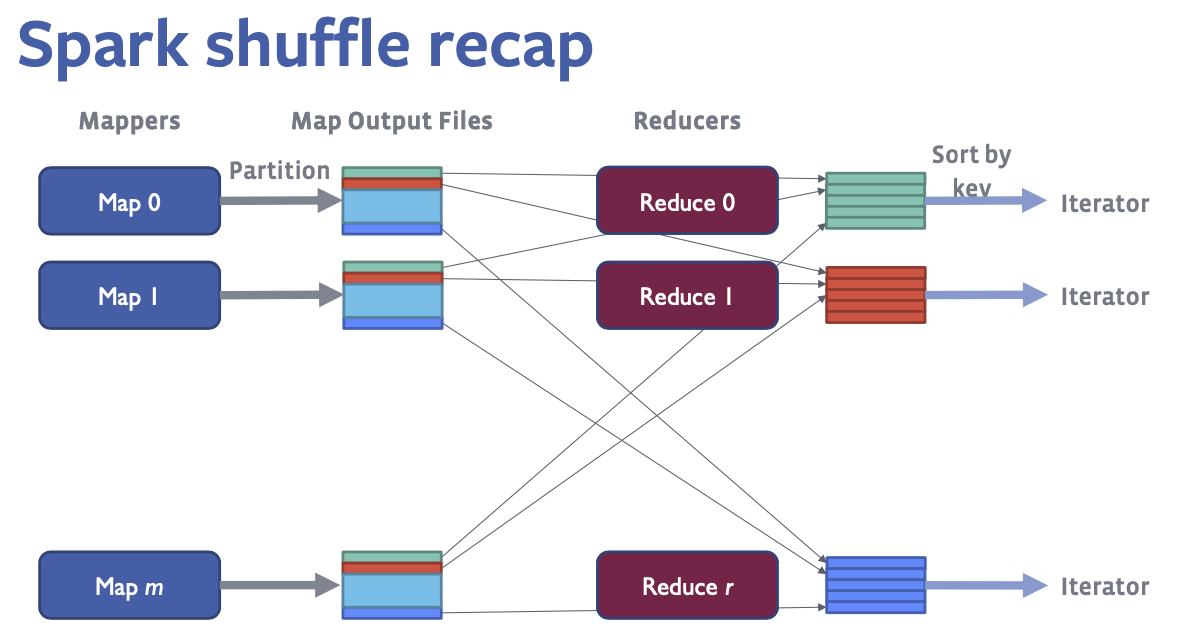
Introduction to Spark Shuffles
Small IO sizes cause low throughput as seek times dominate.
Must increase IO size to maintain the same throughput per TB.
Goals:
- Disk service time
- Average IO size (M * R reads)
- Write amplification: 3x (mappers write, mappers partition read and write, reducers read, and reducers sort)
SOS: merge map outputs to reduce the small I/O problem, but worsens the write amplification.
Cosco
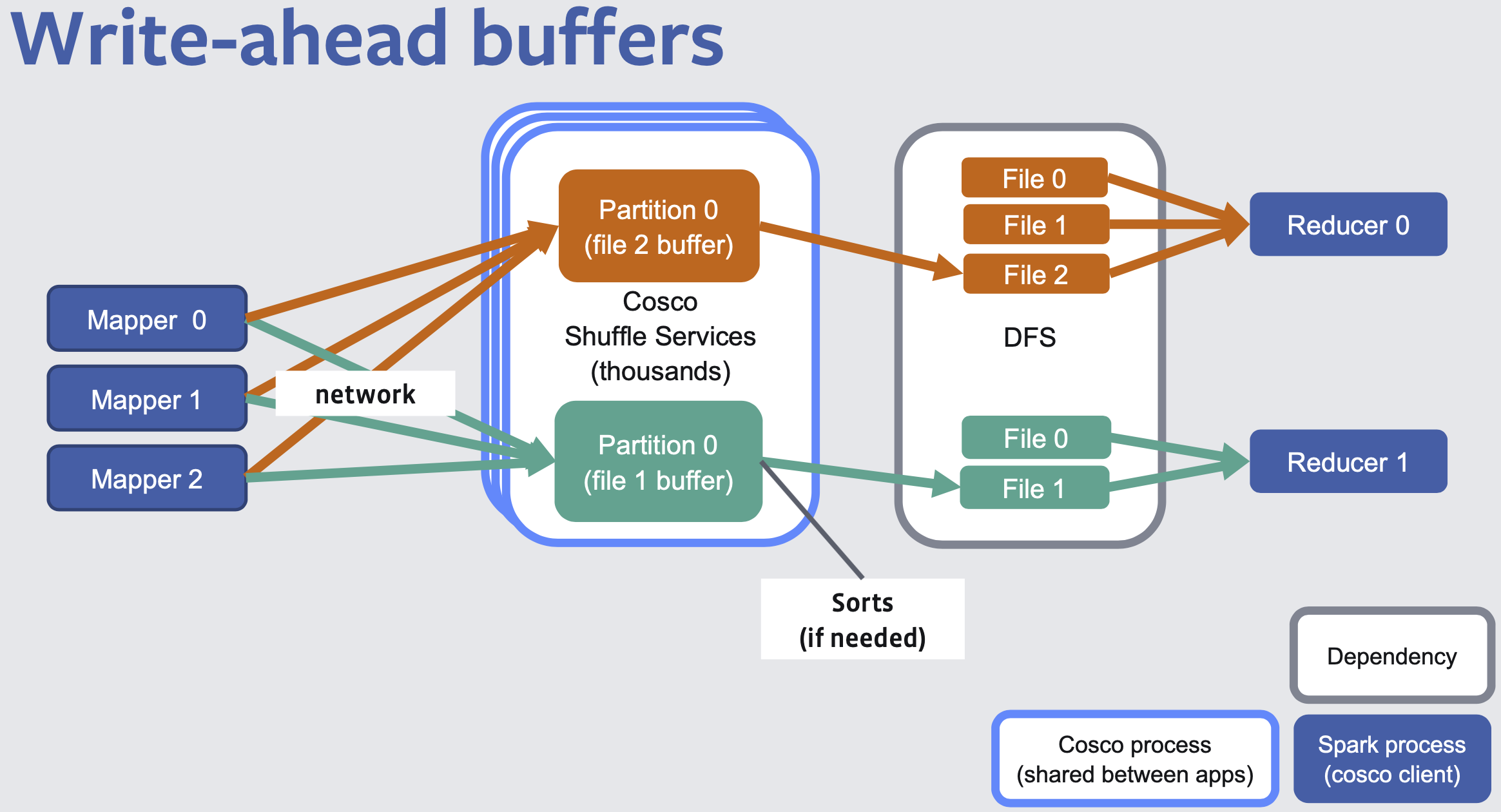
- Mappers share a write-ahead buffer per reduce partition
- Reducers can read the written data sequentially
Solves both the small IOs problem and the write amplification problem.
Mappers transfer the data to shuffle service, and Cosco aggregates data in file buffers, and spills to disk as a single file when it crosses threshold (72MB), and then frees up memory. We can optionally sort. Reducers can read from files sequentially. We eliminates spills from mappers, we can avoid spills on reducer sorts as well.
At least once delivery and deduplication
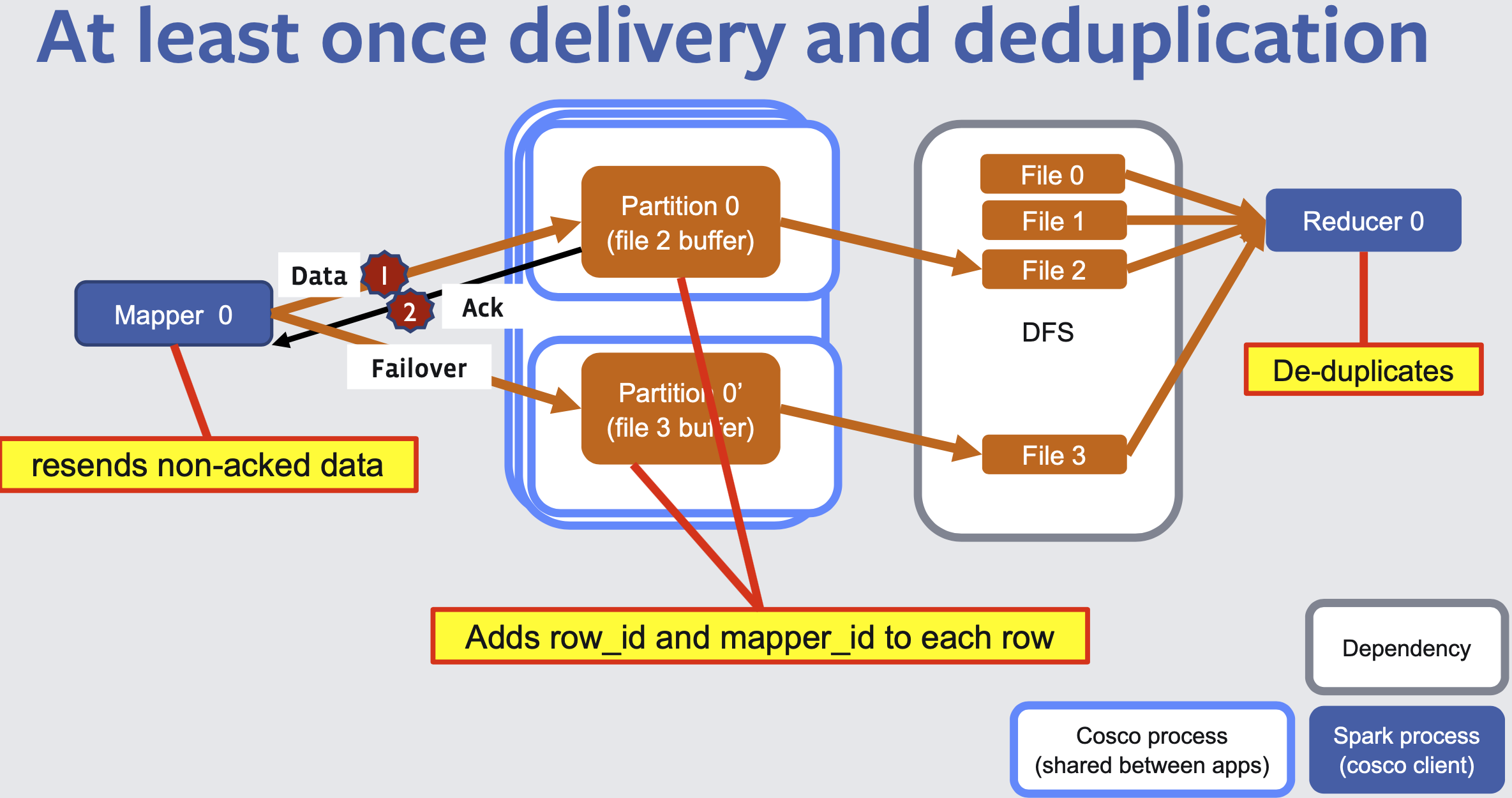
Has write-ahead buffer replication in case of shuffle service failures (therefore two buffers always).
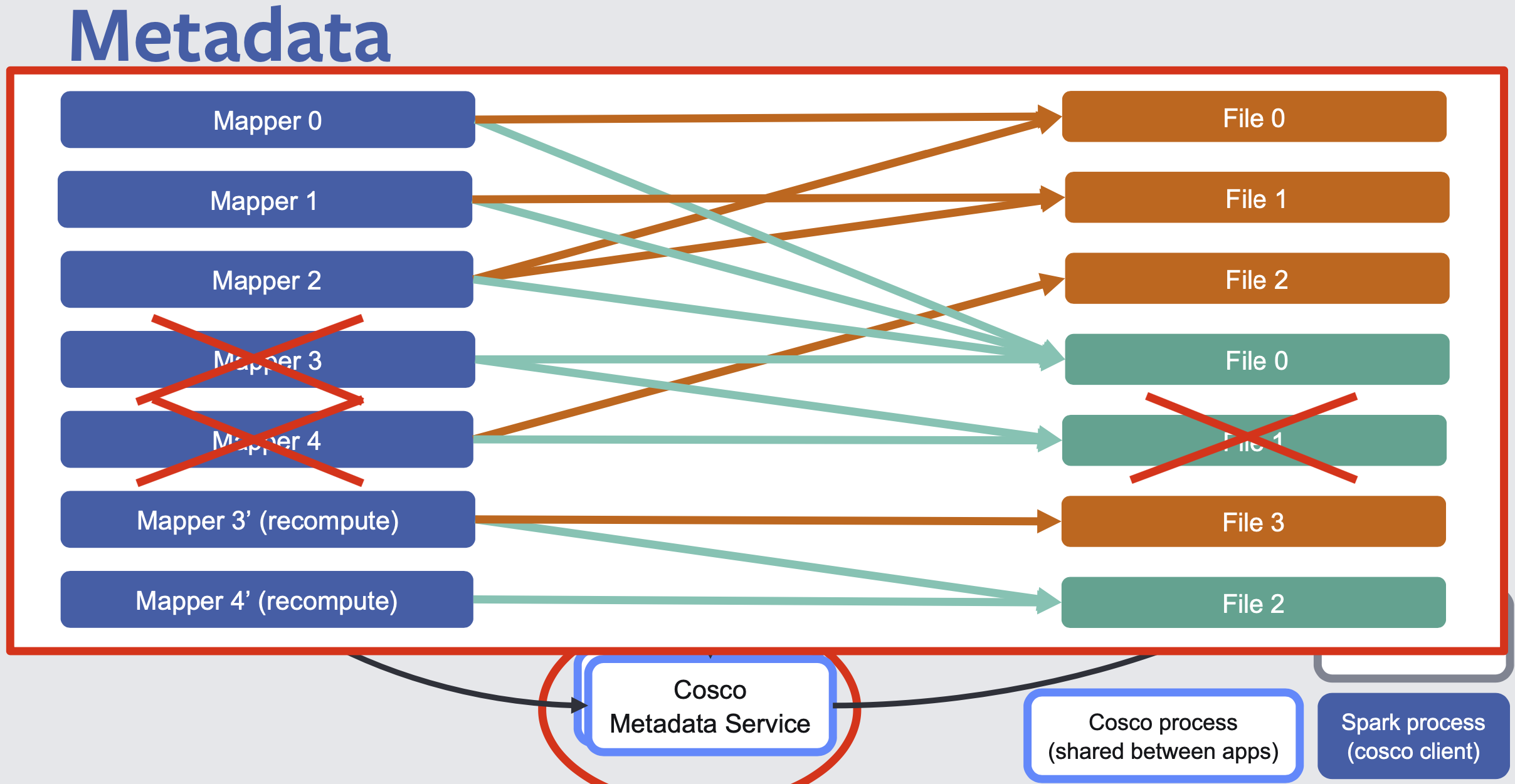
Cosco metadata service keeps many-to-many mapping between mappers and files, as Cosco is not deterministic, and files may get lost so we can restart mappers accordingly.
Shuffle: all to all communication, on disk, strong fault tolerance requirements.
Shuffle I/O grows quadratically with data. Large amount of fragmented I/O requests. But larger task execution reduces shuffle I/O, but increases spill I/O.
SOS merges task outputs into larger shuffle files
- Combines small shuffle files into larger ones
- Keeps partitioned file layout
Number of requests: (M * R) / (merge factor)
SOS shuffle service: a long running instance on each physical node SOS scheduler: keeps track of shuffle files and issues merge requests
Best-effort merge: mixing merged and unmerged files, such that we don’t wait for the completion of map stages.
Merge operation fault-tolerance: fall back to unmerged files. Use large I/O buffers.
